-
Vaser Liposuction
-
Body
-
Breast
-
Face
-
Injectable treatments
-
Hair Transplantation
-
About us
-
Contact
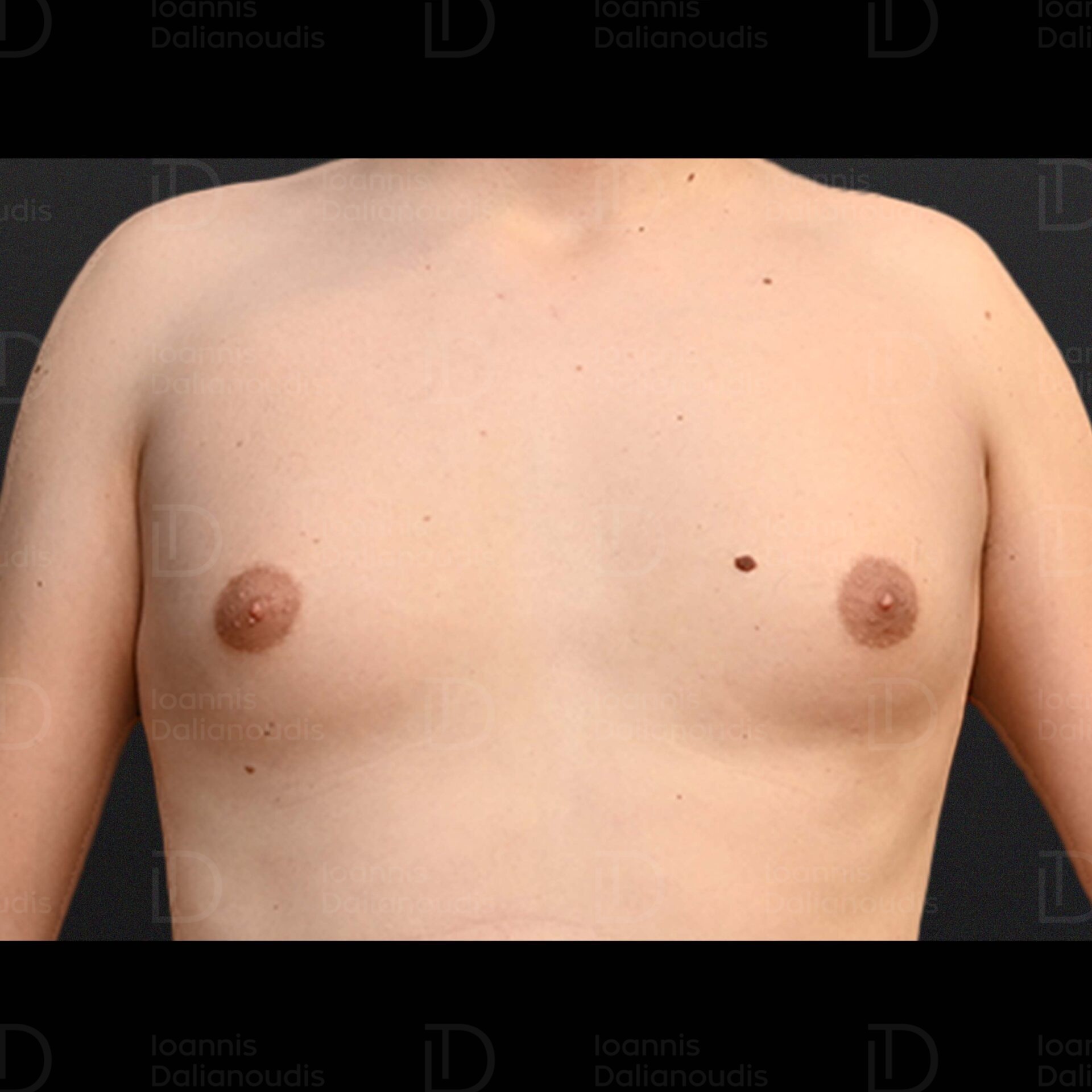
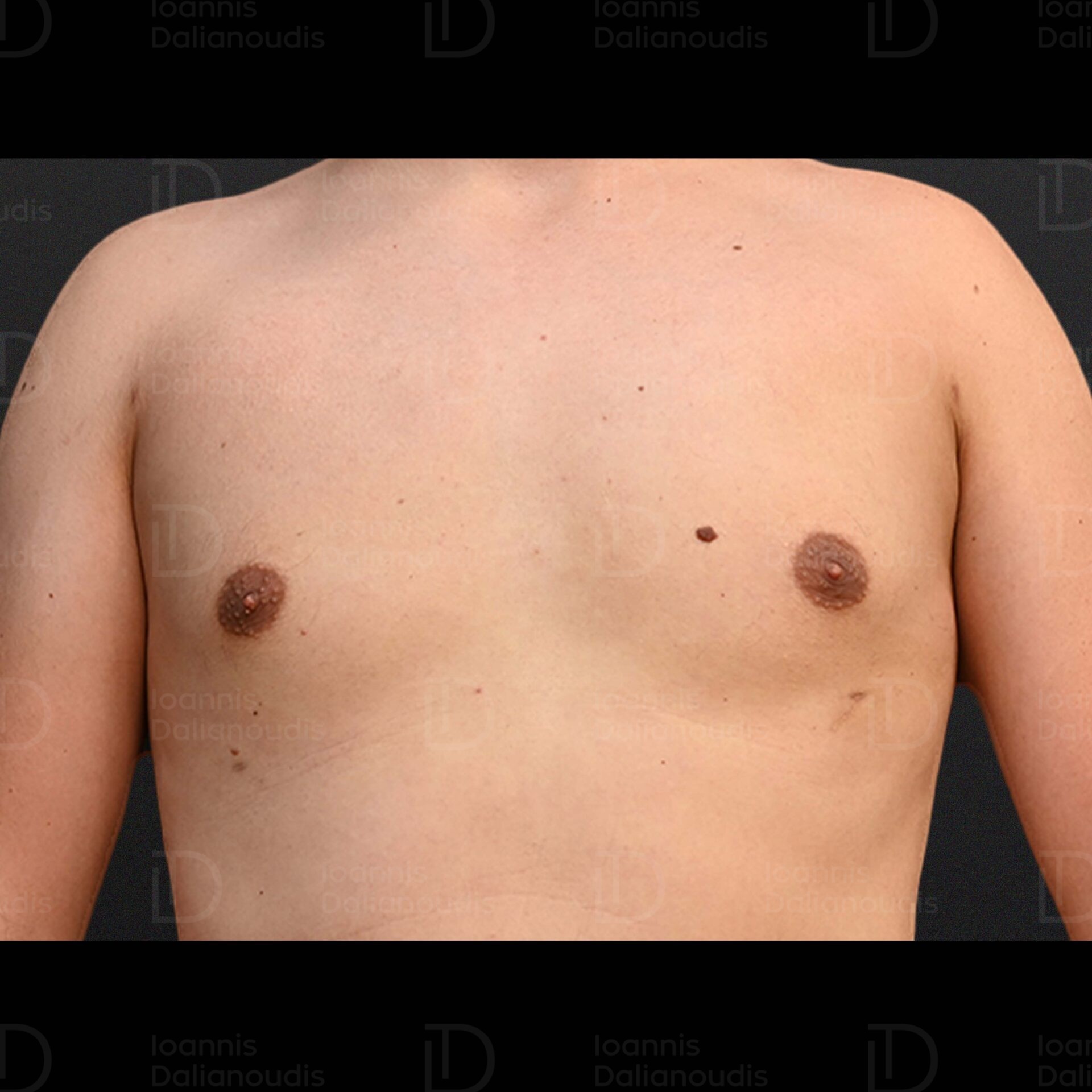
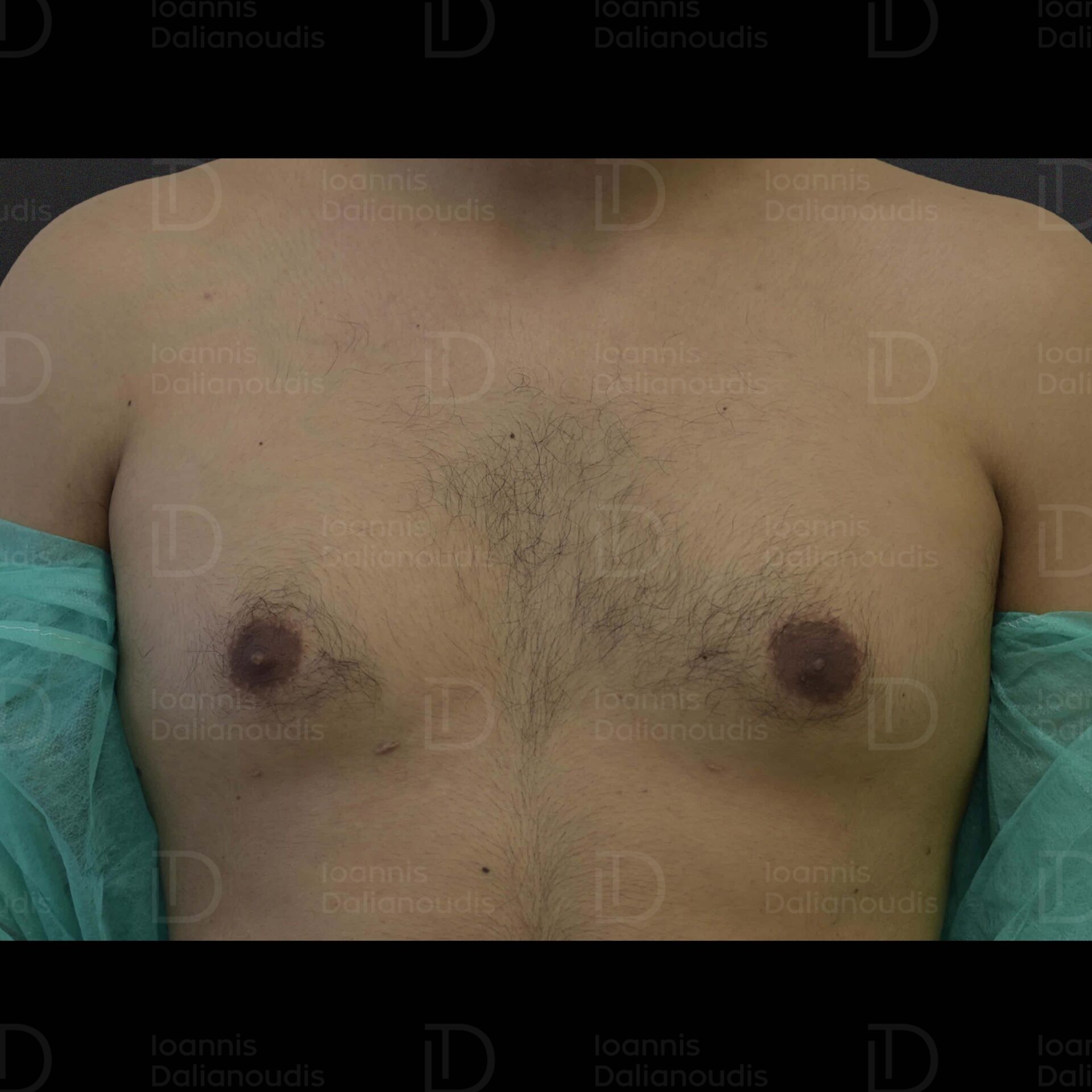
Gynaecomastia: What it is, Ways of Treatment, Costs
Book your appointmentWhat is gynaecomastia?
Gynecomastia, a condition characterized by enlargement of the male breast tissue, can have serious physical and psychological effects on affected individuals. It occurs in both breasts or only one breast and is often accompanied by tenderness or pain.
The condition occurs in men at any age, from infancy to adolescence and adulthood, and may resolve suddenly or persist indefinitely. More than 50% of men will experience this condition in their lifetime.
At a glance
-
Treatment
Gynecomastia Treatment
-
Duration of surgery
1-2 hours
-
Purpose
Removal of excessive breast tissue and fat
-
Target areas
Male Breast
-
Coping with problems
Excessive development of breast tissue giving a feminine appearance to the chest
-
Procedure
Liposuction combined with the removal of breast tissue
-
Anesthesia
Local or General
-
Recovery Time
1 week for return to daily activities, full recovery in 4-6 weeks
-
Results
Reduction in breast size, masculine appearance of the chest
-
Cost
From €1,000
Gynecomastia is caused by several factors, which can be classified into 4 main categories:
1. Hormonal imbalances
Certain conditions, such as puberty, aging, obesity, hypogonadism, and cirrhosis of the liver, can affect hormone levels and cause gynecomastia.
2. Medications
Certain medications, such as anabolic steroids, anti-androgens, estrogens, antidepressants, antipsychotics, and chemotherapy, may be associated with the development of gynecomastia.
3. Obesity
Fat accumulation in men, particularly in the chest area, can lead to an increase in breast size. Obesity can also affect hormone levels and contribute to gynecomastia.
4. Underlying medical conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as hypogonadism, testicular or adrenal tumours, liver cirrhosis, renal failure and thyroidism, can lead to gynaecomastia.
Symptoms of gynecomastia
Gynecomastia manifests itself with various symptoms, which vary in intensity and duration.
- Swelling of the tissue in one or both breasts.
- Unequal or asymmetrical contouring of the breast.
- Swelling, tenderness or pain to the touch.
- Changes in skin texture, such as more "stretched" or stretch marks.
- Bulging and darker nipple algae.
The presence of one or more of the above symptoms is not always a sign of gynecomastia.
Evaluation and diagnosis of gynecomastia
Before deciding on gynecomastia surgery, a thorough evaluation and diagnosis is essential. This procedure usually includes:
Physical examination
The surgeon will examine your breasts to assess the size and extent of the lump and check for any abnormalities, such as lumps or changes in the skin.
Medical history
The surgeon will ask you about any medical conditions that may be associated with gynecomastia and will take into account any medications you are taking, as well as any allergies you may have.
Additional tests
Sometimes, blood tests may be requested to measure hormone levels, check liver function, or rule out other possible causes. Also, mammograms or breast ultrasounds may be used to visualize the breast tissue and identify abnormalities.
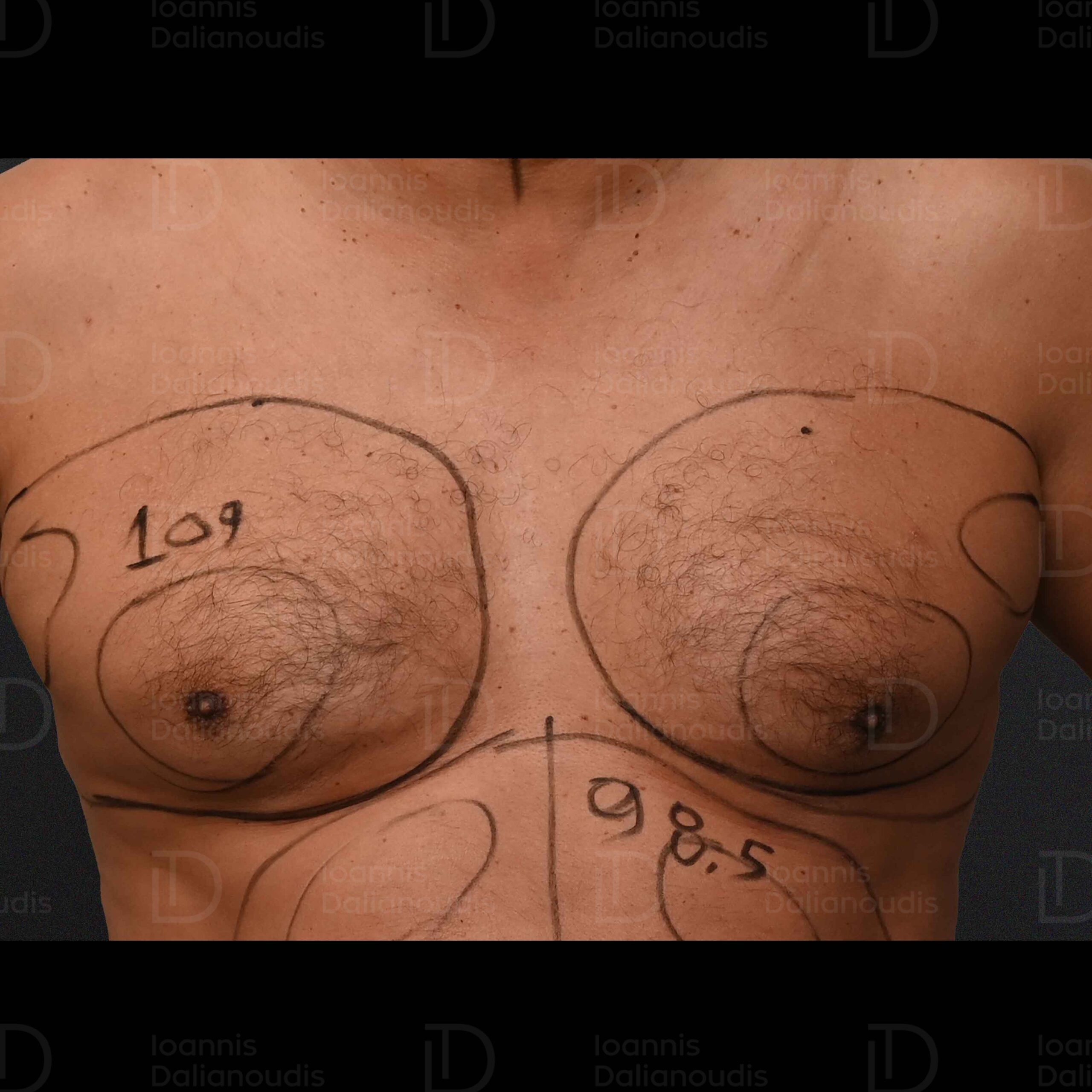
Gynecomastia surgery techniques
Gynecomastia surgery involves several techniques, with the choice of the appropriate one depending on several factors, such as the severity of the condition, the patient's age, and overall health. Below are the techniques that are commonly used:
1. Liposuction
Liposuction is a minimally invasive technique that removes excess fat from the breast. It is commonly used in cases where gynecomastia is mainly due to adipose tissue and is the most common choice of technique. During the procedure, small incisions are made and a thin cannula is inserted to aspirate the fat. However, it has limited effectiveness in case of excessive glandular tissue or loose skin.
Vaser liposuction
At our clinic, liposuction is performed with the Vaser technique, which uses advanced ultrasound technology to liquefy and selectively suction out adipose tissue. Vaser targets fat while leaving other important tissue intact, giving you the precise contour you want with less pain, post-operative bruising, and recovery time than other liposuction techniques.
2. Excision
Excision is the ideal solution for gynecomastia cases involving swollen glandular tissue and sagging skin. During the excision procedure, the surgeon removes excess glandular tissue and reposition the nipple and areola (lower part of the nipple periphery) to create a more natural appearance. This technique may leave slightly more noticeable scarring compared to liposuction and may lengthen recovery time by a few days, but it is particularly effective for treating severe gynecomastia.
3. Combination technique
In cases where gynecomastia involves a combination of excess fat, glandular tissue and skin laxity, the combined technique is used. This approach combines both liposuction and excision to address all aspects of the condition comprehensively. The surgeon will tailor the technique to the needs of each patient, ensuring the best possible outcome.
4. Two-time surgery
In very difficult cases, surgery is performed in two times. First, liposuction with Vaser is performed to achieve tightening. After six months the case is reassessed and if necessary glandular tissue or even skin will be removed in cases with a lot of sagging.
Treatment without surgery
In most cases, non-surgical treatments are recommended as the first approach to managing gynecomastia. These treatments include hormone therapy, discontinuation of medications that may be causing the condition, and lifestyle modifications such as weight loss and exercise.
Medical management options for gynecomastia include medications such as selective estrogen receptor modulators SERMs such as tamoxifen and raloxifene or aromatase inhibitors such as anastrozole and letrozole.
These drugs act by regulating estrogen levels or blocking the activity of estrogen receptors, thereby reducing the swelling of breast tissue size. However, the effectiveness of medication varies between individuals and side effects such as nausea, headache and libido complications can limit tolerance and adherence to treatment.
However, these medications do not always provide the desired results, especially in cases of severe swelling of glandular tissue, and surgery is often the most effective way to treat gynecomastia.
Lately, some tips and products such as special physical exercises, homeopathic remedies and herbal creams are being advertised on the internet as natural ways of dealing with the problem of gynecomastia. It is important to know, that there is no scientific research or serious clinical study that documents their effectiveness.
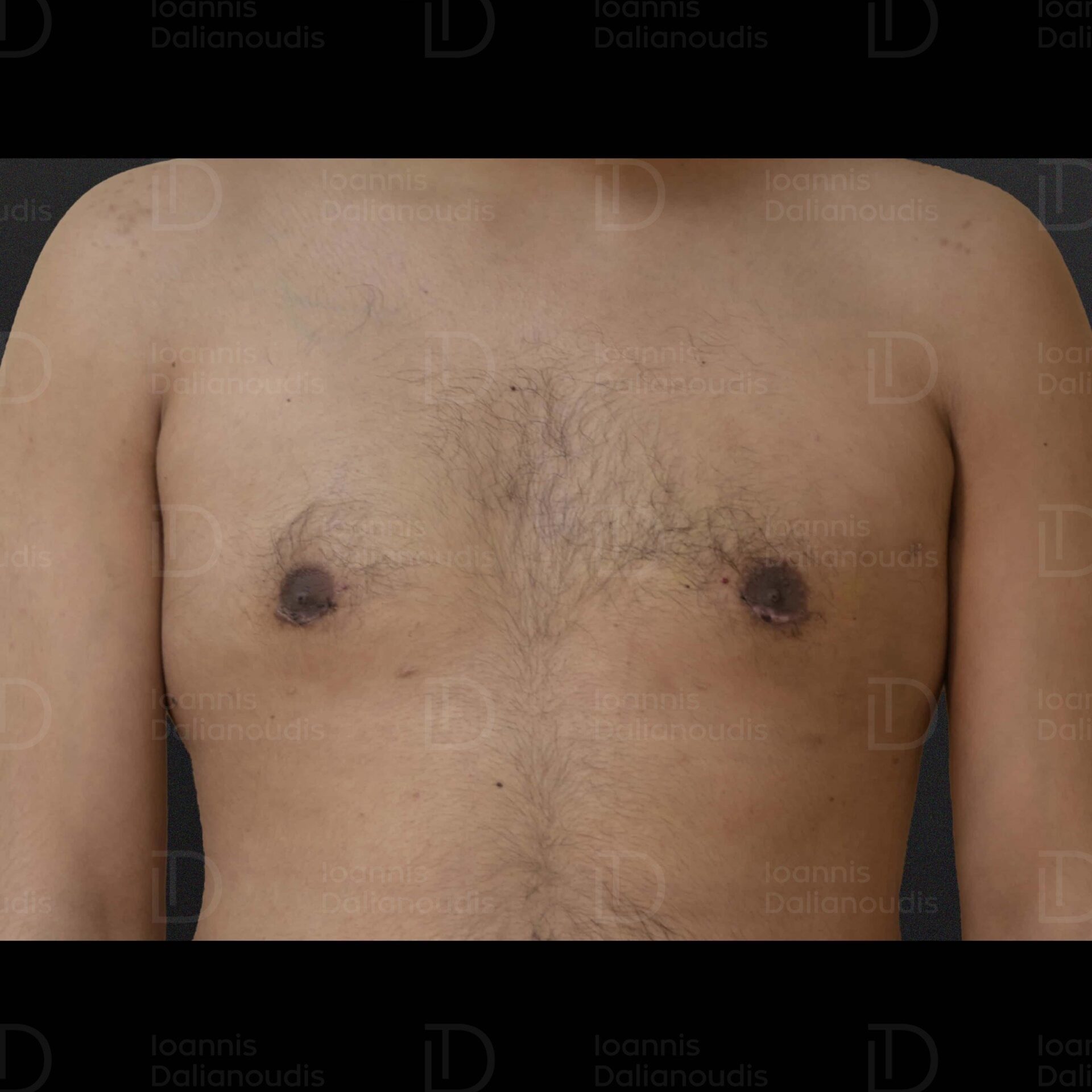
What are the side effects of surgery?
Surgical complications after gynecomastia surgery are usually mild, transient and easily treatable with medication and proper care. They usually involve:
- Bruising and bleeding
- Fluid accumulation
- Swelling
- Itching
- Scarring
- Loss of sensation
Cost
The cost of surgery is individualized. The severity of the condition, the amount of correction required and the surgical technique used all affect the complexity of the surgery and therefore the cost. An indicative price for the cost of gynecomastia surgery is €2,000. If cost is a concern for you, at our clinic we maintain affordable prices and offer payment facilities with interest-free instalments by credit card.
Useful questions
01
When do scars go away after surgery?


Scarring is expected due to the body's reaction to the incisions of surgery and is part of the healing mechanism. By using medication and avoiding the sun you will reduce their appearance and speed up healing. In addition, limit hand movements, lifting heavy objects and exercise until approved by the plastic surgeon. The scars gradually fade over time and within a year they will be almost invisible.
02
Is gynecomastia surgery painful?


Gynecomastia surgery is performed under anesthesia and patients do not feel any pain during the procedure. However, some discomfort and pain is expected during the recovery period, which is managed with prescription painkillers.
03
How is gynecomastia surgery performed?


A detailed analysis of the procedure is given below:
1. Gynaecomastia surgery is usually performed under general anaesthesia and very rarely under local anaesthesia.
2. Location of the incision:
- The operation involves small incisions around the areola or in the submastric or submastric groove. A submastric incision is usually preferred to minimise the visibility of the scar.
3. Tissue removal and contouring:
Remove excess adipose and glandular tissue. In our clinic, liposuction is performed using the Vaser technique in order to achieve tightening in the area and a masculine and balanced contour that fits your body anatomy.
4. Nipple and areola repositioning:
- If necessary, the surgeon will reposition the nipple and areola to ensure a better aesthetic appearance.
5. Closure of the incision:
- Once the desired contour is achieved, the incisions are closed with sutures and the surgeon may use drains to prevent fluid build-up.
6. Recovery and follow-up:
- You will be given instructions and prescribed medication to help you cope with discomfort and feel more comfortable after the operation. You will then return home.
04
What can I expect after my gynecomastia surgery?


Expect some pain or discomfort after the procedure, treated with painkillers. Swelling and bruising are to be expected after the procedure. Take the anti-inflammatories and antibiotics given to you by your doctor and the swelling will gradually subside within a few days. If you do not have absorbable stitches, the surgeon will remove them after a few days. Recovery time varies depending on the extent of the surgery. Usually, most patients return to daily activities after 7 to 10 days.
05
How will I have a smooth recovery after surgery?


How will I have a smooth recovery after surgery? (Η3)
After gynecomastia surgery, it is important to follow your surgeon's instructions to have a smooth recovery. Here are some general tips:
- Take your prescribed medications as directed.
- Take your prescription medications as prescribed.
- Apply cold compresses for the first 1-2 days to reduce swelling.
- Wear the compression bandage you were given.
- Avoid strenuous physical activity.
- Do not lift heavy objects.
- Do not stretch or raise your arms above shoulder height.
- Sleep on your back with your head slightly elevated.
- Drink plenty of fluids and eat healthily.
If you notice any signs of infection, such as persistent redness, swelling, pain, fever or pus coming out of the incisions, contact your surgeon immediately.
06
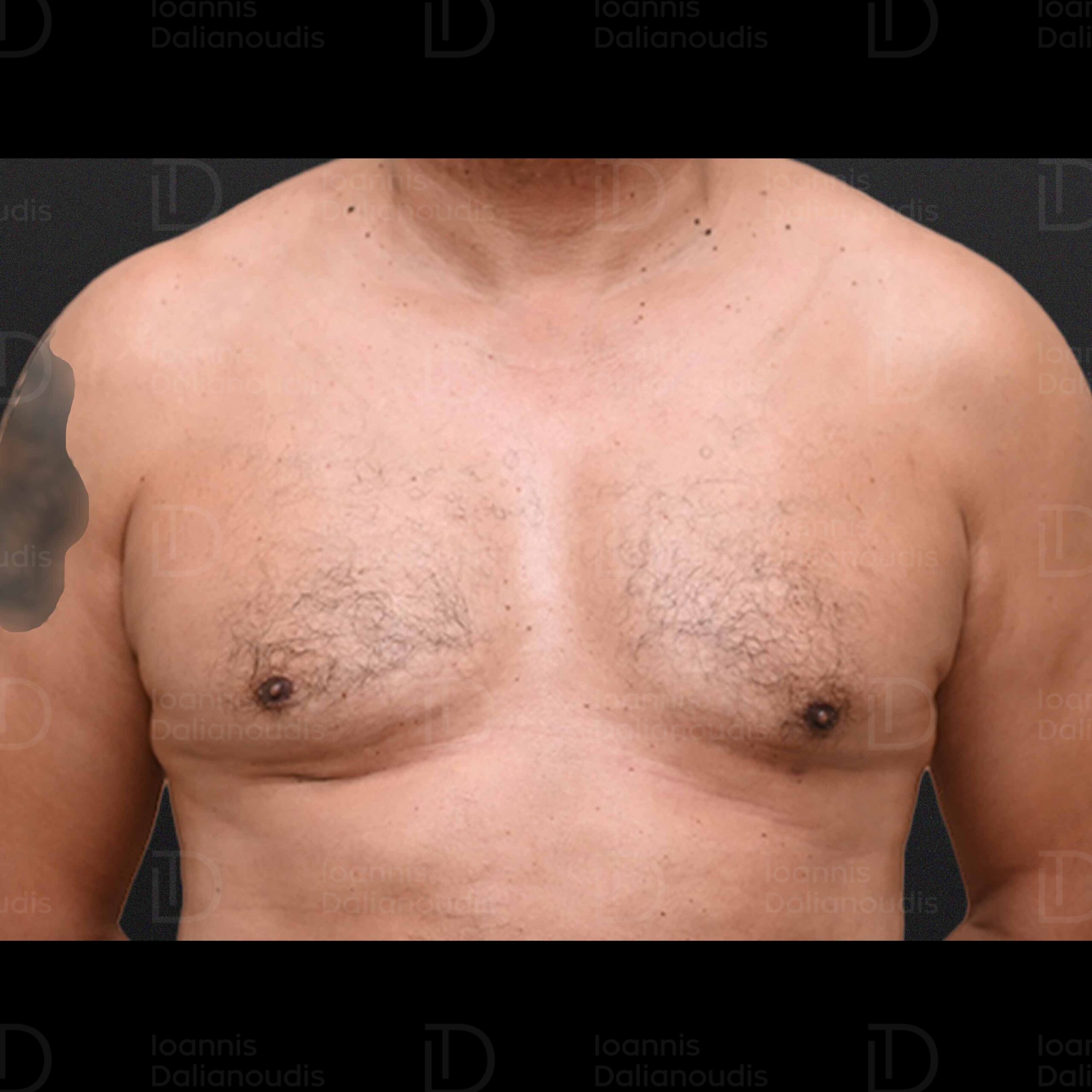
Are the results of the surgery permanent?


Gynaecomastia surgery can provide permanent results. Removal of glandular tissue and contouring of the breast leads to long-lasting changes. However, some factors such as weight gain, ageing, heredity and unhealthy lifestyle may affect the outcome of the surgery.
07
What is pseudogynecomastia (lipomastia)?


Gynecomastia is a benign swelling of breast tissue in men and is due to enlarged glandular tissue with or without adipose tissue. Pseudogynecomastia or otherwise called lipomastia is due only to excessive fatty deposition.
Pseudogynecomastia
- Cause : Increase in fatty tissue
- Texture : Soft, pliable
- Sensitivity: Usually painless
- Age: More common in overweight and obese men
Gynecomastia
- Cause : Hypertrophy of glandular tissue
- Texture : Hard, fibrous
- Sensitivity : May be painful
- Age : More common in teenagers or men over 50

Who is the doctor
Dr. Ioannis Dalianoudis is an experienced plastic surgeon, a graduate of the University of Ioannina with a professional career that includes work in several countries, including France, Denmark and Ireland. Specializing in plastic, reconstructive and cosmetic surgery, he trained in Germany in facial cosmetic surgery. He has performed a variety of procedures including eye surgery, facelift, rhinoplasty, bariatric surgery recovery and body contouring. In addition, he is a member of the "European Board of Plastic Surgery (EBOPRAS)" and is dedicated to patient satisfaction, making him a trusted choice for plastic surgery seekers. His dedication to patient satisfaction, his expertise and his vast experience in the Greek and international arena make him a reliable choice for those looking for plastic surgery.
Contact
Form

* Fields marked with * are mandatory
* Fields marked with * are mandatory
Also see